
Maximising Results with GHRP-6 and Ipamorelin Peptide Stacking
Peptide stacking is a sophisticated method that involves the deliberate selection and combination of specific peptides to enhance their individual effects, leading to superior results
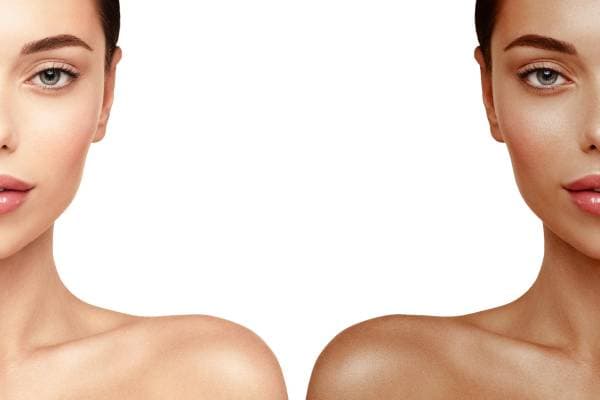

Achieving a sun-kissed glow has always been a desirable aesthetic, and thanks to scientific advancements, some peptides are now known to enhance tanning abilities. Melanotan 1 and Melanotan 2 are two popular peptides that have gained significant attention in scientific communities. In this article, we will delve into the depths of these peptides, uncover their benefits, discuss their differences, and provide insights into their usage.
Melanotan 1 and 2 are synthetic analogues of the hormone α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH). These peptides work by stimulating melanin production, the pigment responsible for skin, hair, and eye colour. When administered, they activate the melanocortin receptors in the body, promoting tanning and other related effects.
Both of the MT peptides are still under scientific investigation. Currently it has not been approved for use in humans by the FDA. Direct SARMs is committed to providing high purity sarms and peptides for medical research purposes only.
References:
[1] https://jamanetwork.com/journals/ jamadermatology/fullarticle/ 480676
[2] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ pubmed/15262693
[3] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ pubmed/8637402
[4] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ pmc/articles/PMC3663356/
Disclaimer: We do not supply sarms or peptides to any individual under the age of 21. You must be a licensed and qualified healthcare practitioner. Our team of dedicated professionals are committed to providing an extensive range of products used ONLY in the process of laboratory research by responsible trained and professional individuals. All products listed on this website (direct-sarms.com) and provided through Direct Sarms are intended for laboratory research purposes only. The products listed on this website are NOT for human or animal consumption or ingestion of any kind.

Peptide stacking is a sophisticated method that involves the deliberate selection and combination of specific peptides to enhance their individual effects, leading to superior results
Maximizing Healing and Rejuvenation: Exploring the Benefits of TB500 and GHK-Cu Peptides Combined In the rapidly changing field of biomedical research, peptides have become key
Worldwideshipping

Visa/Mastercard/Zelle
Cryptocurrency /Transfers

Safe and Secure Shopping

We Distribute
From

YOU MUST BE OVER 21 YEARS IN ORDER TO USE THIS WEBSITE. All of the products are to be handled only by properly trained and qualified LABORATORY or RESEARCH professionals.